Networking
Information about Platform and MicroVM networking.
Platform networking options
Users are responsible for bringing and configuring their own hardware and networking solutions.
We recommend the following network considerations for the platform:
- A private subnet for MicroVMs. Each MicroVM will request addresses on boot. Reserving public IPv4 addresses is unnecessary and wasteful for MicroVMs which will be part of a Kubernetes cluster.
- A single reserved IP for each cluster's load-balanced API endpoint. This can be public or private, depending on whether you wish the cluster to be exposed. A unexposed cluster with a private address, and suitable access such as a VPN, will be preferable to most.
- Starting the
flintlockdservices either within a private subnet, or ensuring that the service is secured with authentication.
MicroVM networking modes
Flintlock can create MicroVMs in two different network modes.
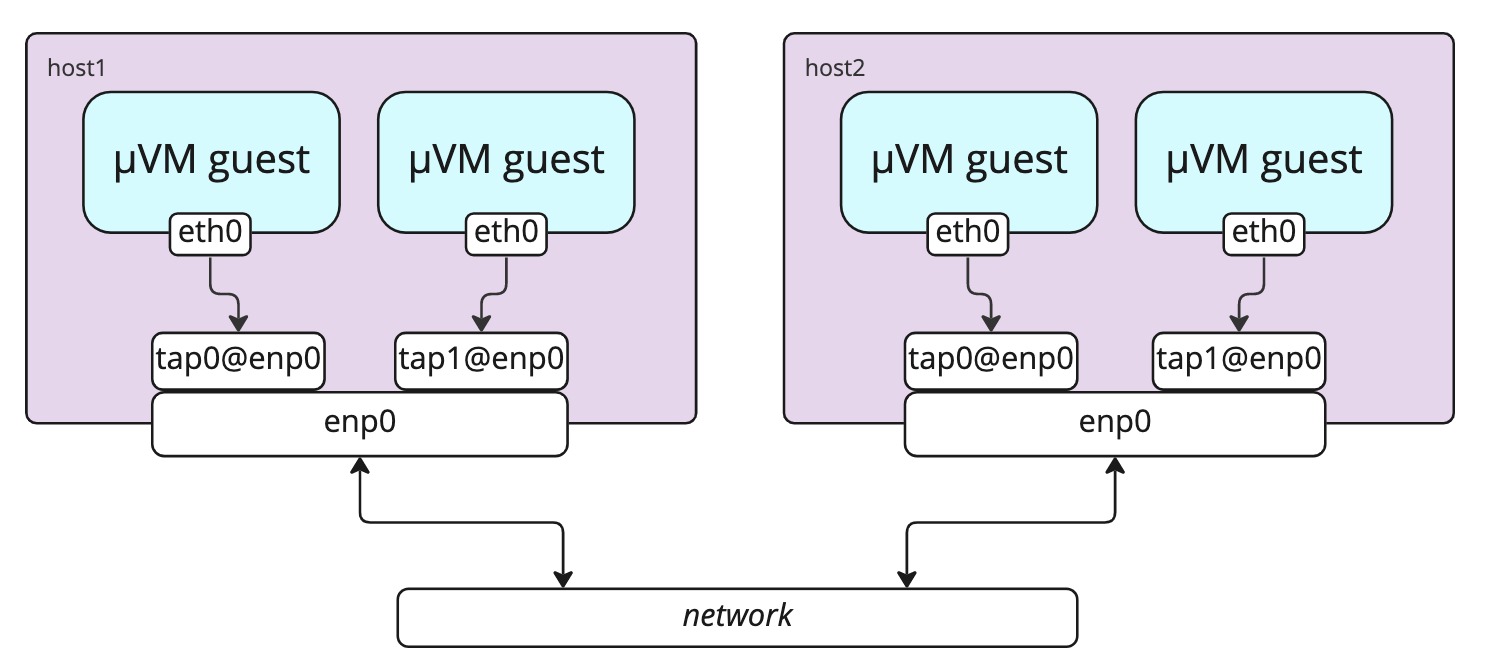
Macvtap mode
On devices with the capability, MicroVMs can be created with their default interface
mapped to macvtap interfaces in the host.
The devices are created in bridge mode, enabling inter-microvm traffic directly
between the taps without it passing through the host interface.
macvtap is the default option.
Configure flintlockd to be ready to create macvtap devices by starting the service with
the following in /etc/opt/flintlockd/config.yaml:
parent-iface: enp0 # where the value is a wired interface on the host
When creating MicroVMs directly via flintlock, ensure the spec contains the following:
...
"interfaces": [
{
"device_id": "eth1",
"type": 0 // 0 for macvtap
}
]
...
When creating MicroVMs as part of a cluster via CAPMVM, ensure the spec contains the following:
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: MicrovmMachineTemplate
spec:
template:
spec:
networkInterfaces:
- guestDeviceName: eth1
type: macvtap
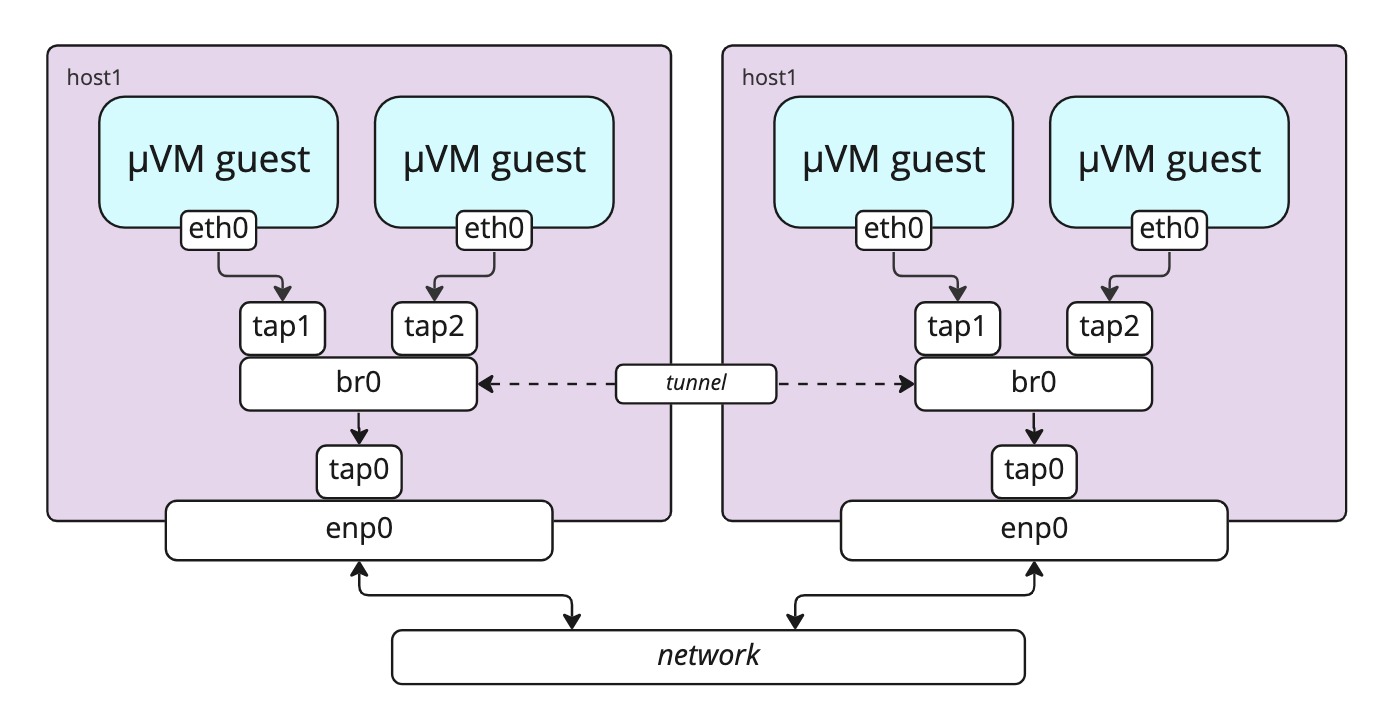
Bridge mode
Flintlock can optionally create MicroVMs in which the default interface within the guest
is mapped to a tap device attached to a bridge on the host.
Configure flintlockd to be ready to use a bridge to create tap devices by starting the service with
the following in /etc/opt/flintlockd/config.yaml:
bridge-name: br0 # where the value is a bridge to a host interface
Both bridge-name and parent-iface can be set in /etc/opt/flintlockd/config.yaml.
The decision is made at MicroVM create time depending on which is requested via the API.
When creating MicroVMs directly via flintlock, ensure the spec contains the following:
...
"interfaces": [
{
"device_id": "eth1",
"type": 1 // 1 for tap
}
]
...
When creating MicroVMs as part of a cluster via CAPMVM, ensure the spec contains the following:
apiVersion: infrastructure.cluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1
kind: MicrovmMachineTemplate
spec:
template:
spec:
networkInterfaces:
- guestDeviceName: eth1
type: tap